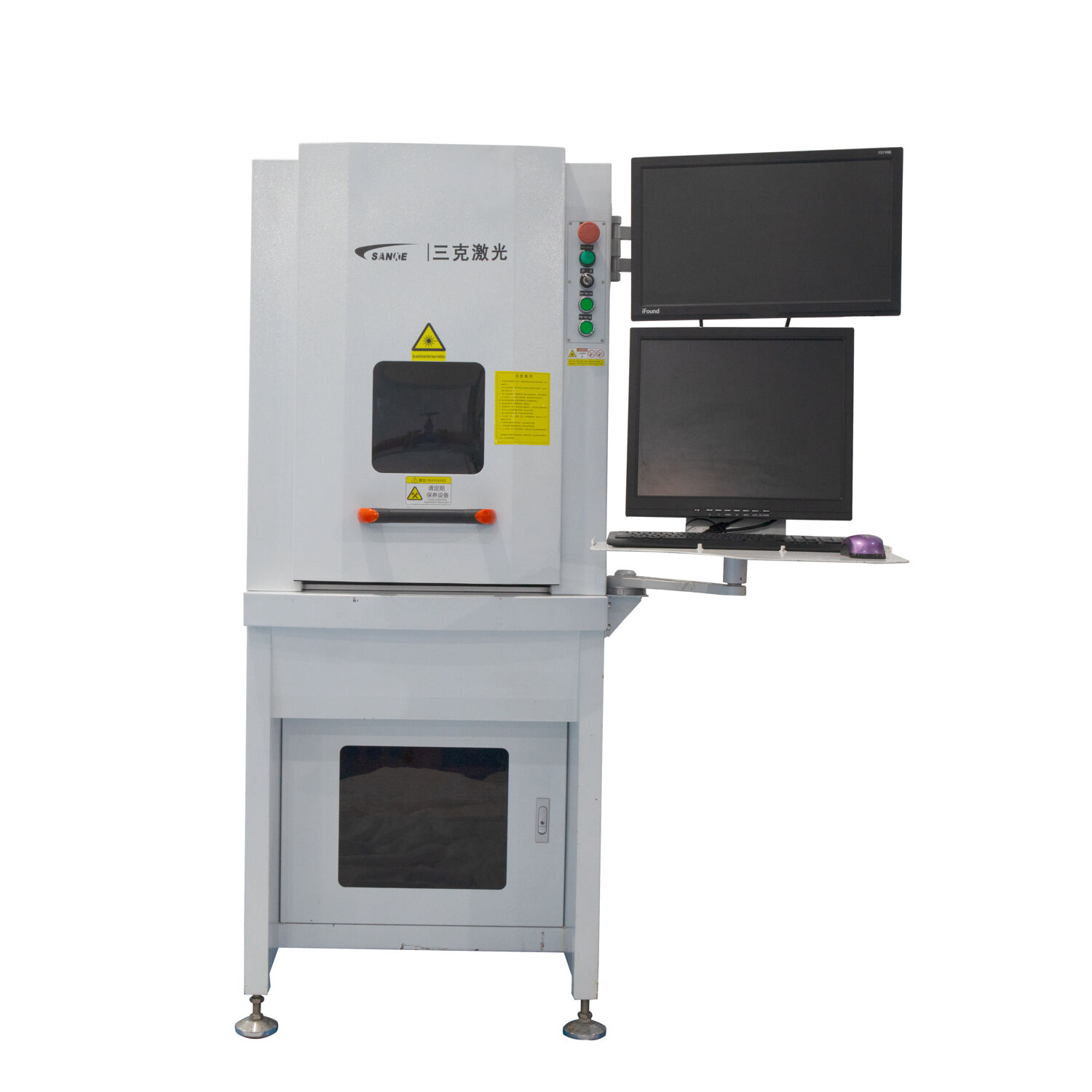
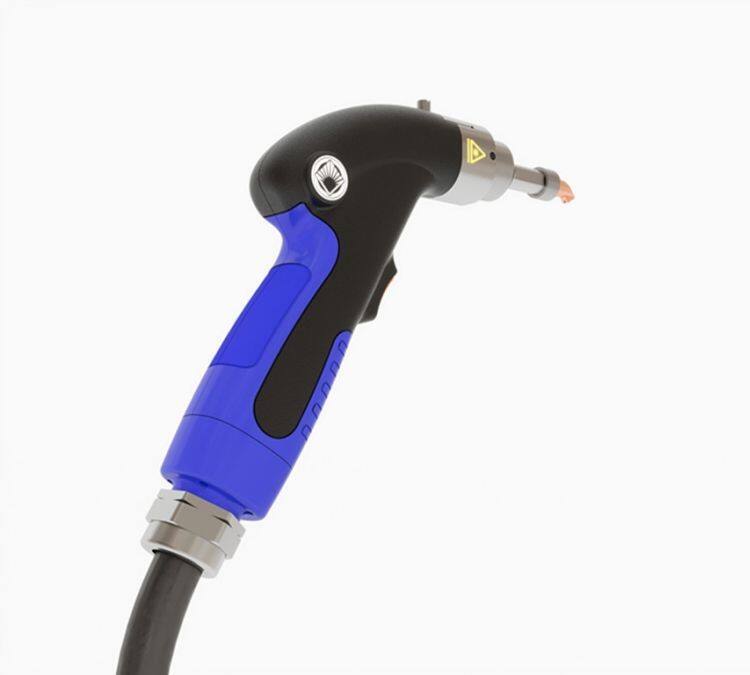
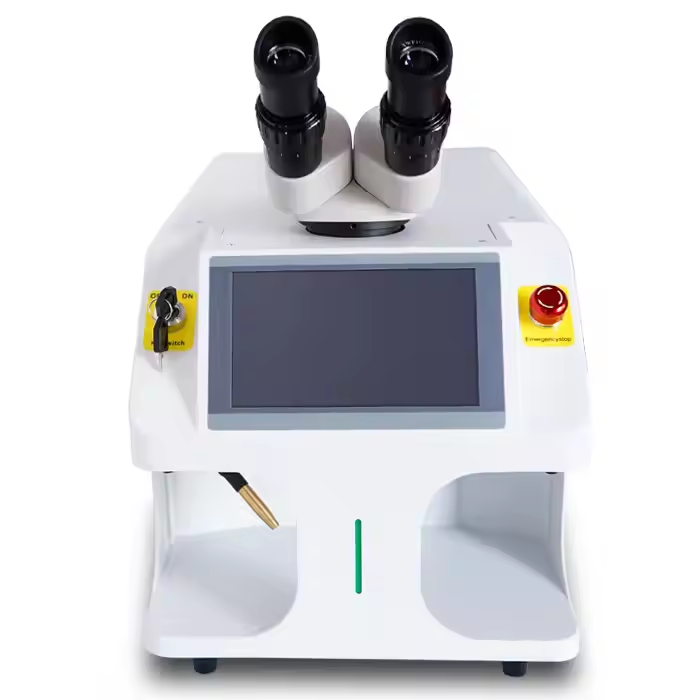
Superior Material Compatibility and Versatility
Automotive laser welding excels in processing diverse material combinations that enable innovative vehicle designs while meeting stringent performance requirements across various applications. The technology effectively joins dissimilar materials including aluminum to steel, stainless steel to carbon steel, and advanced high-strength alloys to conventional materials, creating hybrid structures that optimize weight, strength, and cost characteristics. This material versatility supports lightweighting initiatives critical for fuel efficiency improvements and emission reduction goals throughout the automotive industry. Automotive laser welding systems accommodate material thickness ranges from thin foils under 0.1 millimeters to heavy sections exceeding 25 millimeters, providing flexibility for everything from delicate electronic components to robust structural elements. The technology processes both coated and uncoated materials effectively, handling galvanized steels, aluminum alloys with protective treatments, and specialty coatings without degradation or quality issues. Advanced beam shaping capabilities allow optimization of laser energy distribution for specific material combinations, ensuring optimal penetration and fusion characteristics regardless of alloy composition or thermal properties. Automotive laser welding supports various joint configurations including butt joints, lap joints, T-joints, and complex three-dimensional geometries that traditional welding methods cannot achieve reliably. The process adapts to different material surface conditions, welding through oils, oxides, and other contaminants that would prevent successful joining with conventional techniques. Programmable parameters enable manufacturers to develop optimized welding schedules for new materials and alloy combinations as automotive technology evolves toward advanced materials and sustainable construction methods. The technology handles reflective materials like aluminum and copper alloys through specialized laser wavelengths and beam delivery systems designed for challenging optical properties. Heat treatment effects remain minimal due to controlled thermal input, preserving engineered material properties such as precipitation hardening, work hardening, and heat treatment conditions essential for component performance. These material compatibility advantages position automotive laser welding as the preferred technology for manufacturers developing next-generation vehicles that require innovative material solutions for enhanced performance, efficiency, and sustainability.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES