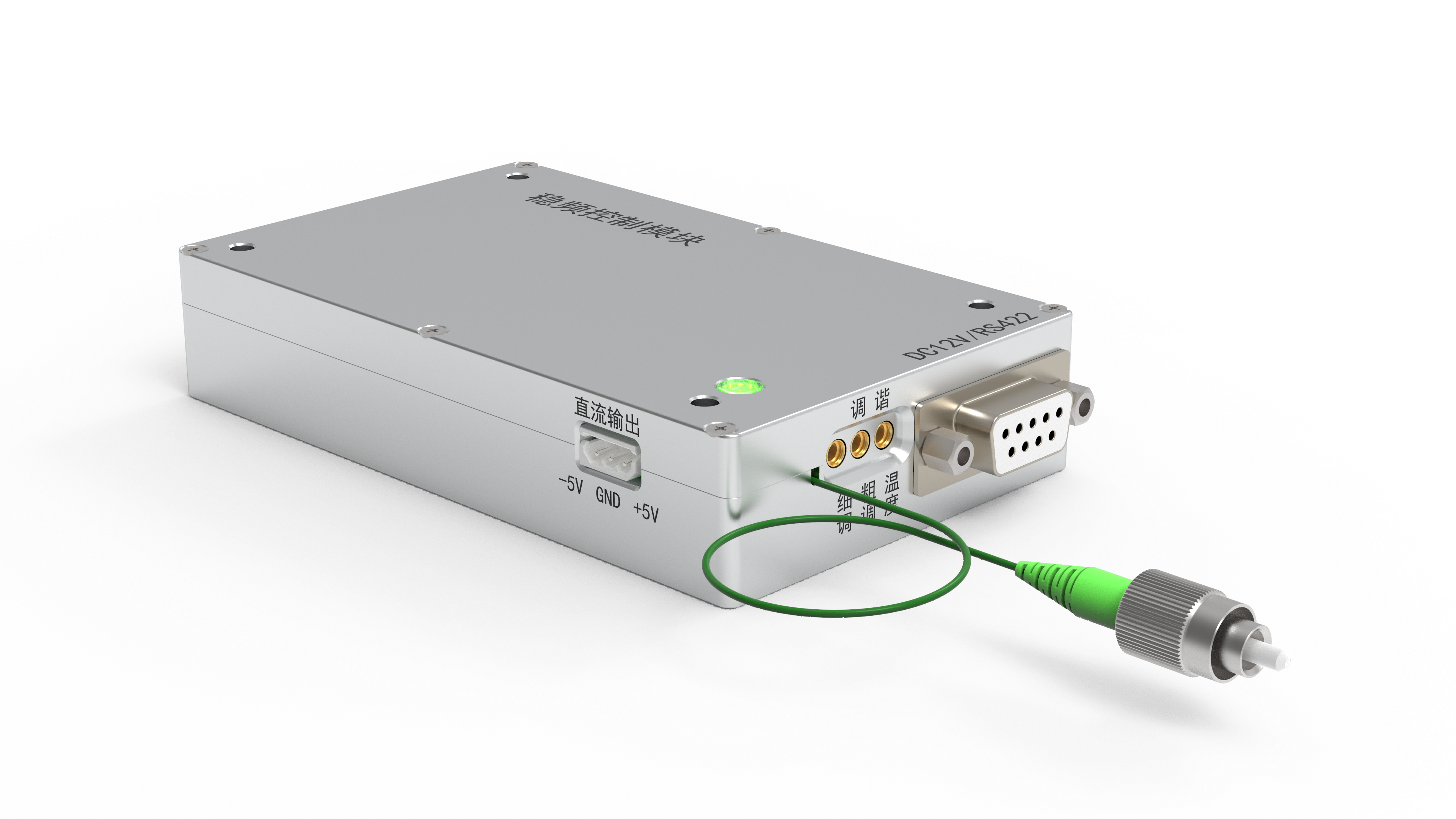
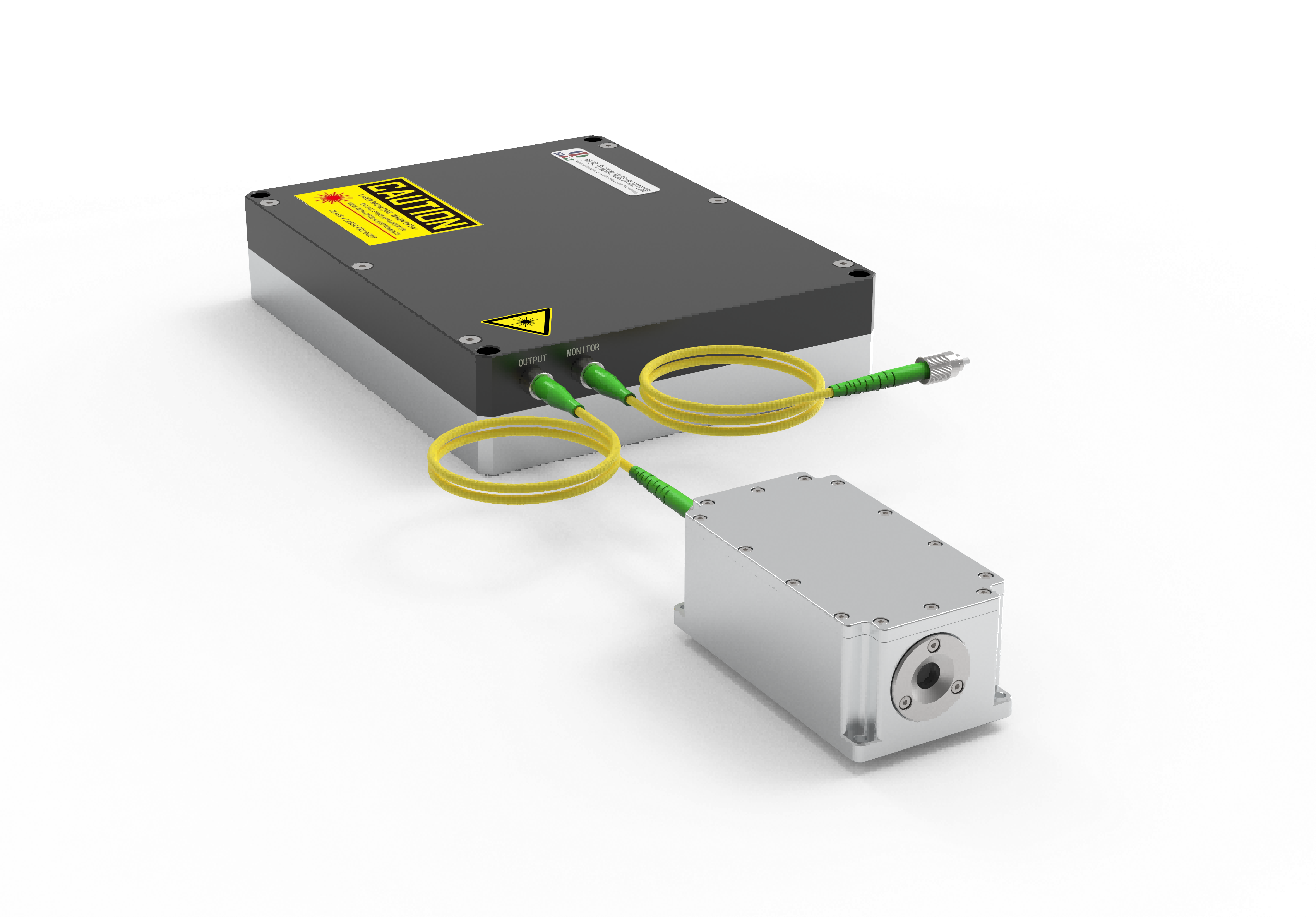
fiber laser light source
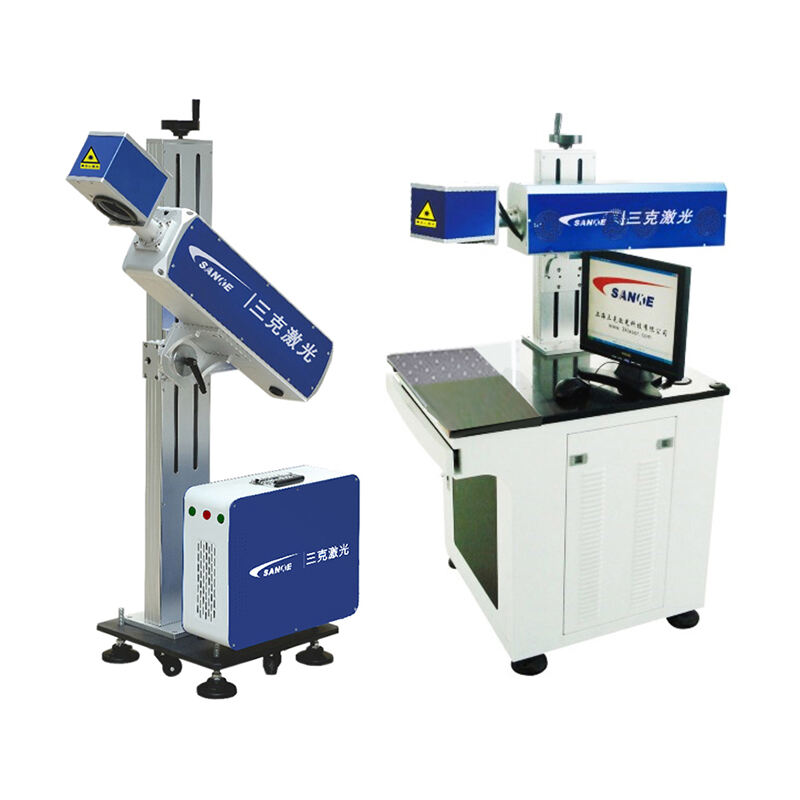
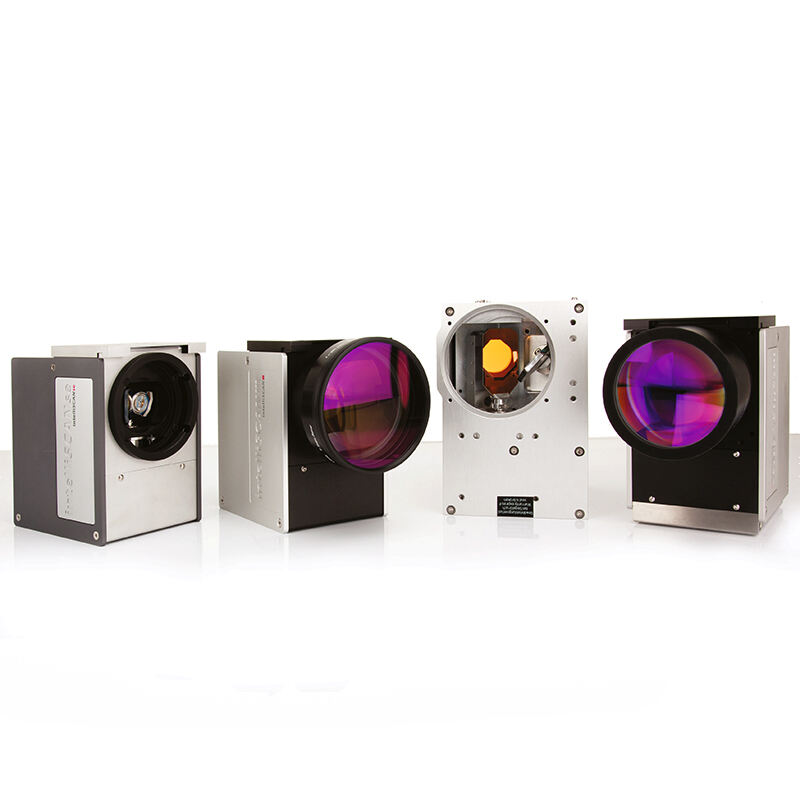
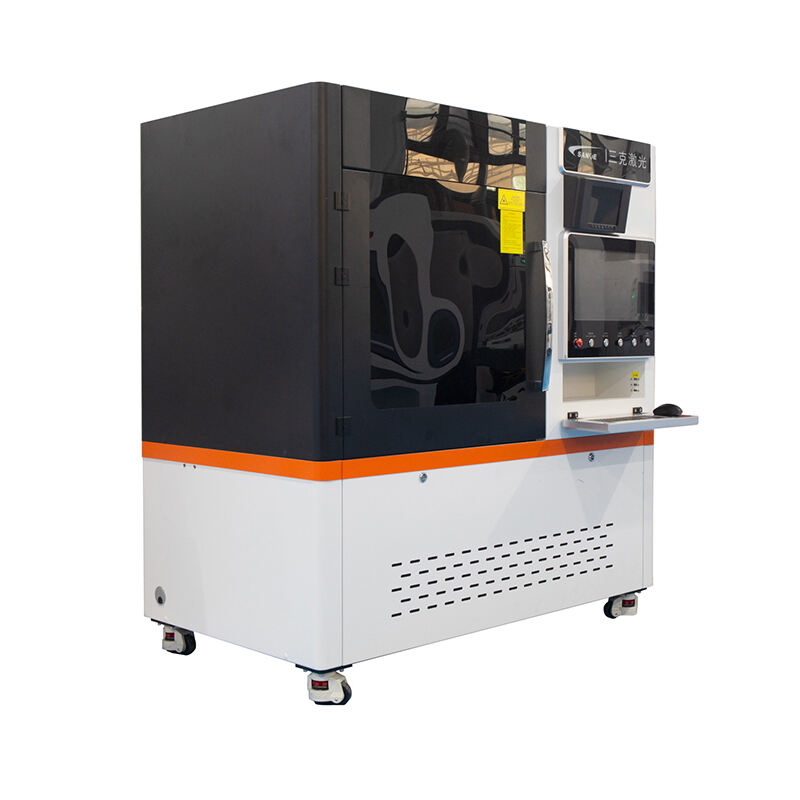
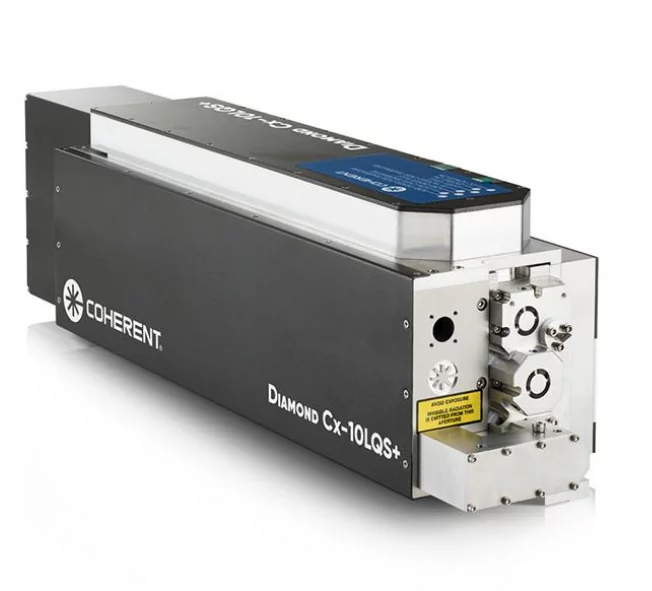
A fiber laser light source represents a cutting-edge optical technology that generates coherent light through stimulated emission within an optical fiber medium. This innovative system utilizes rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, or thulium as active dopants within the fiber core to produce highly concentrated laser beams. The fiber laser light source operates by pumping energy into the doped fiber through semiconductor diodes, creating population inversion and subsequent laser emission. The main functions of a fiber laser light source include precise material processing, telecommunications signal amplification, medical procedures, and scientific research applications. Its technological features encompass exceptional beam quality, compact design, and remarkable efficiency levels that surpass traditional laser systems. The fiber laser light source delivers consistent power output across various wavelengths, making it suitable for diverse industrial and commercial applications. The system incorporates advanced cooling mechanisms and sophisticated control electronics to maintain optimal performance under demanding operational conditions. Key components include the pump diodes, doped fiber gain medium, optical isolators, and beam delivery systems that work together to produce reliable laser output. The fiber laser light source excels in applications requiring high precision, such as micro-machining, welding, cutting, and marking operations across multiple industries. Manufacturing sectors benefit from its ability to process materials ranging from metals and plastics to ceramics and composites with exceptional accuracy. Medical applications utilize the fiber laser light source for surgical procedures, therapeutic treatments, and diagnostic imaging due to its precise control and minimal thermal damage characteristics. Research institutions employ these systems for spectroscopy, metrology, and advanced optical experiments. The fiber laser light source continues to evolve with improvements in power scaling, wavelength versatility, and integration capabilities, positioning it as a fundamental technology for future optical applications across numerous sectors.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES