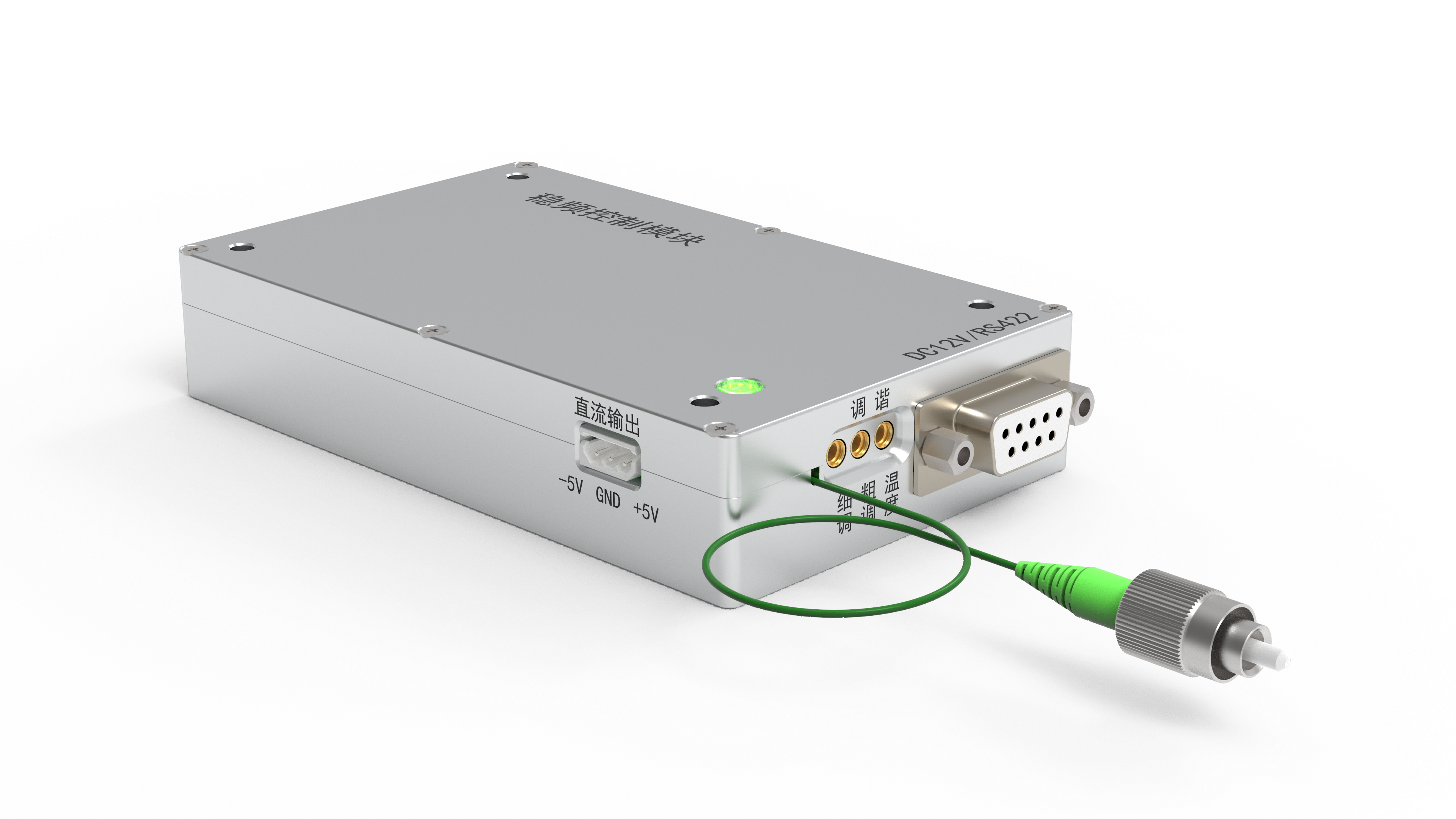
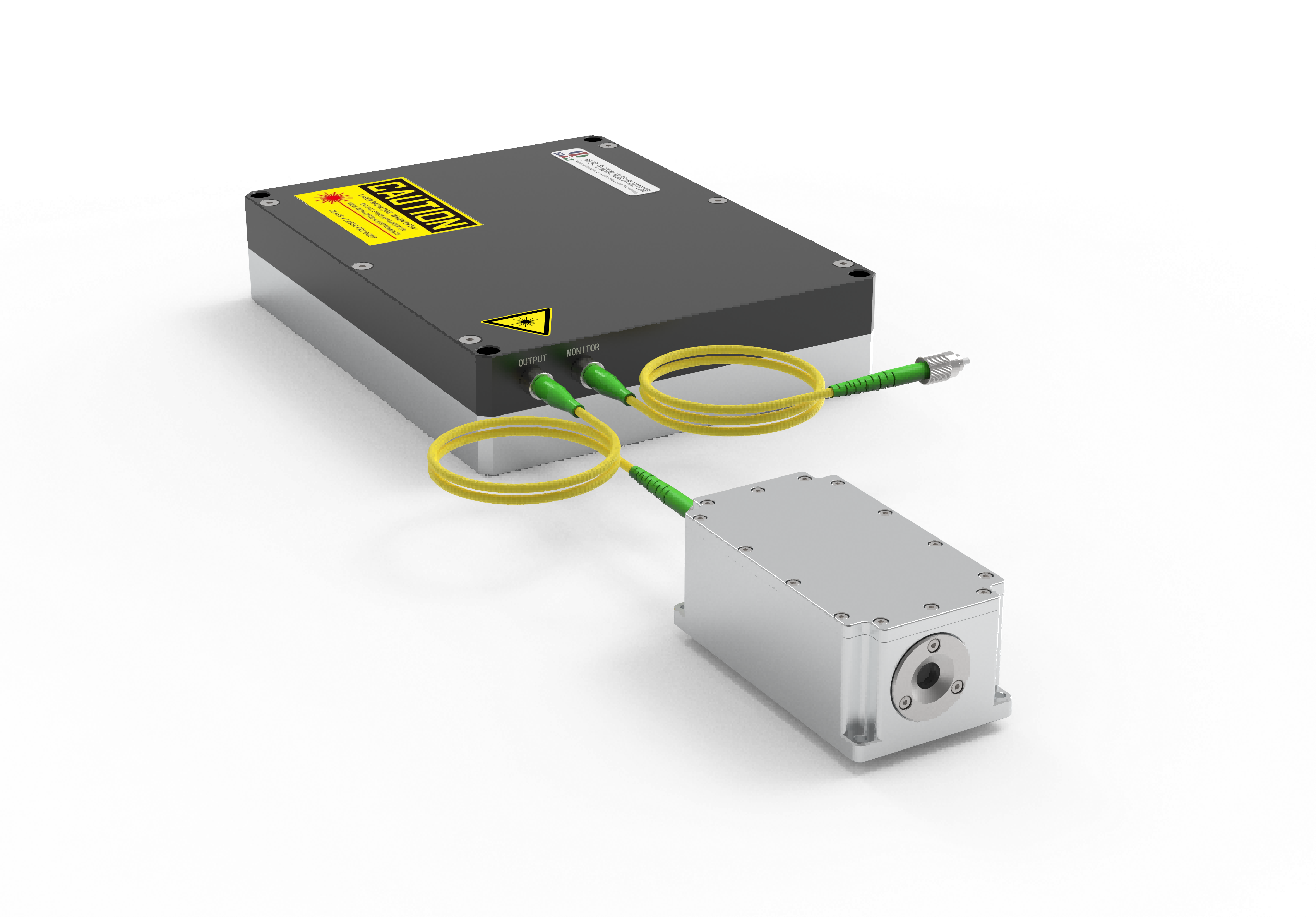
a source of laser light sends rays
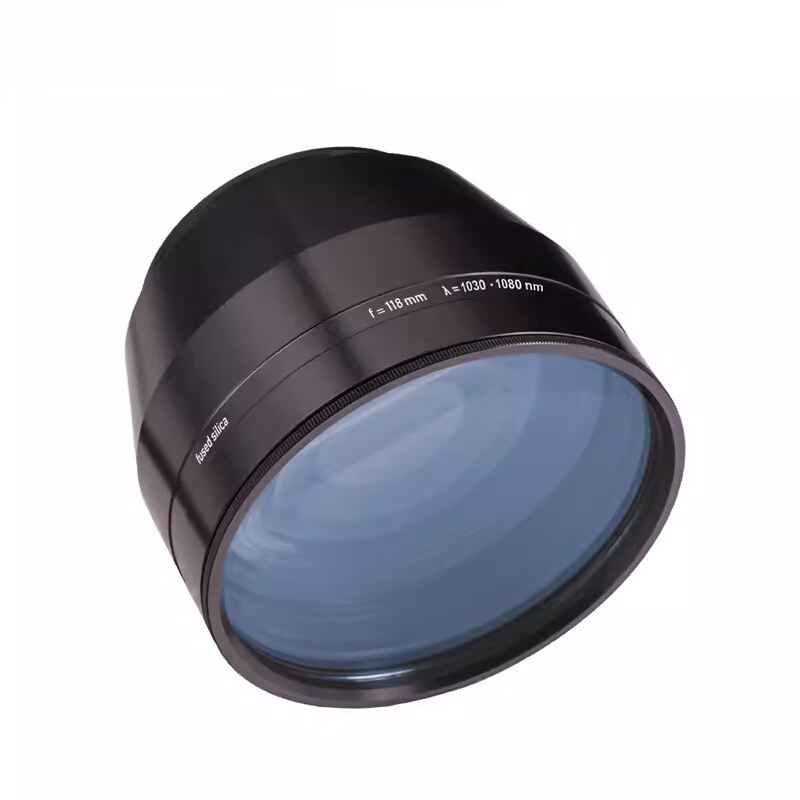
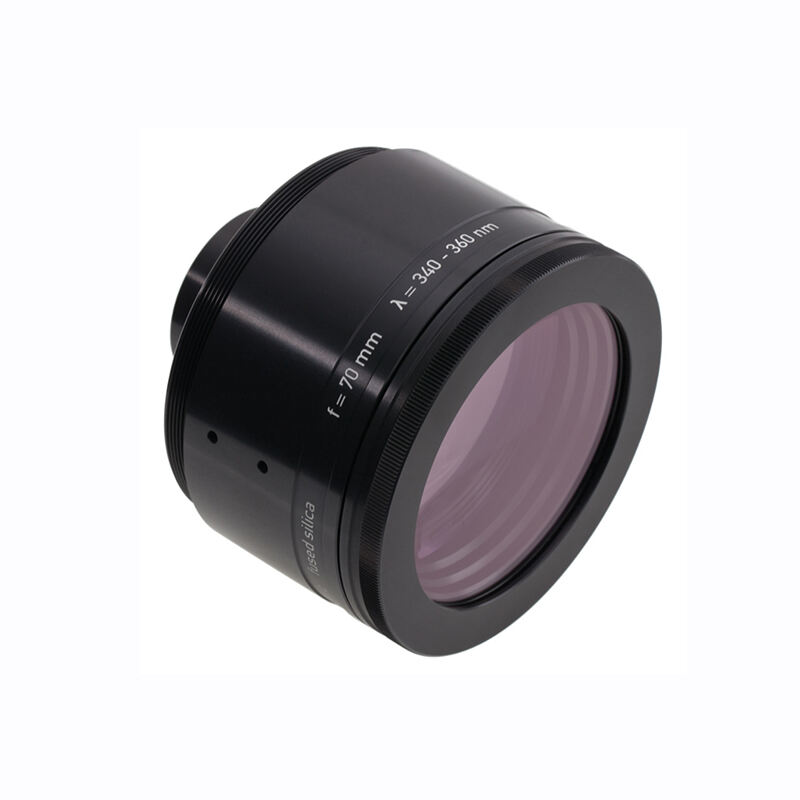
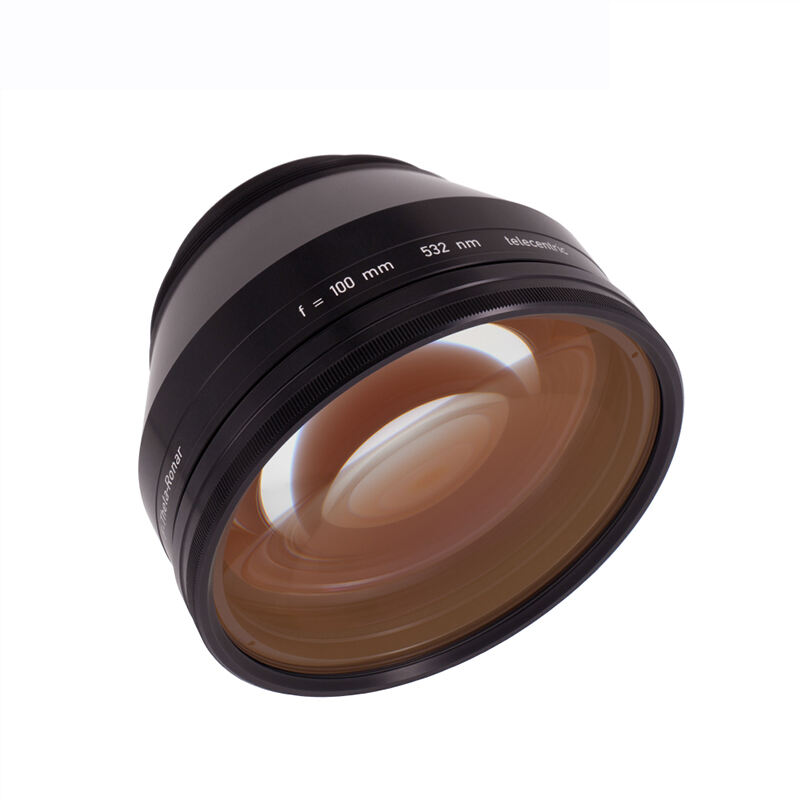
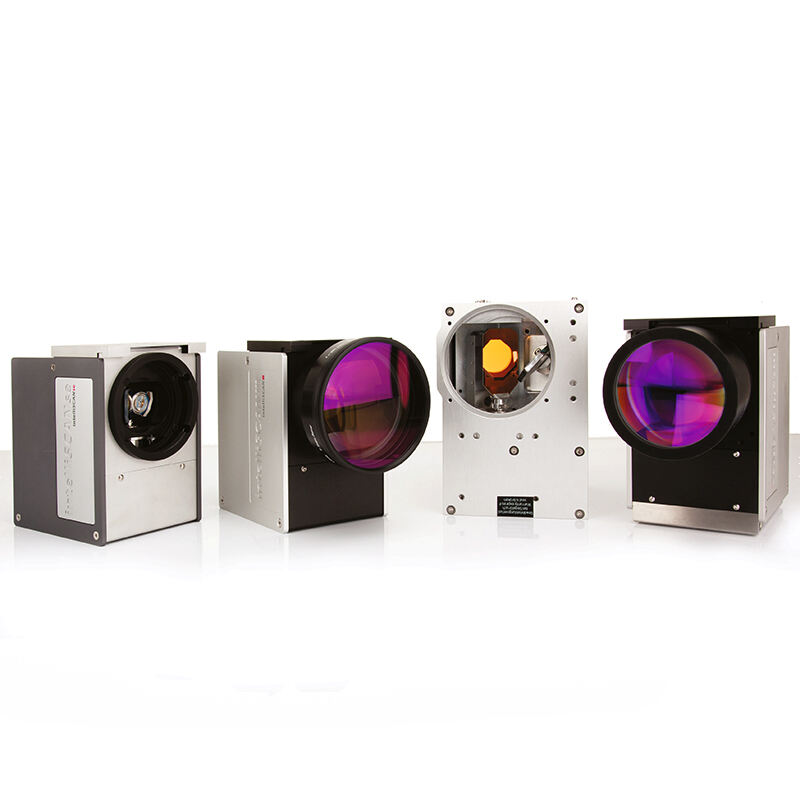
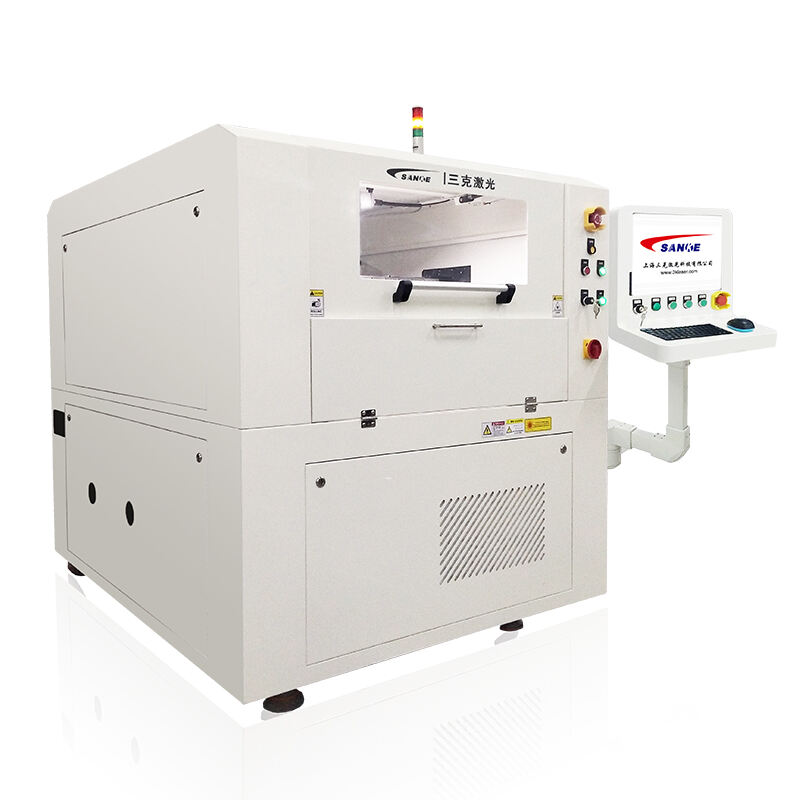
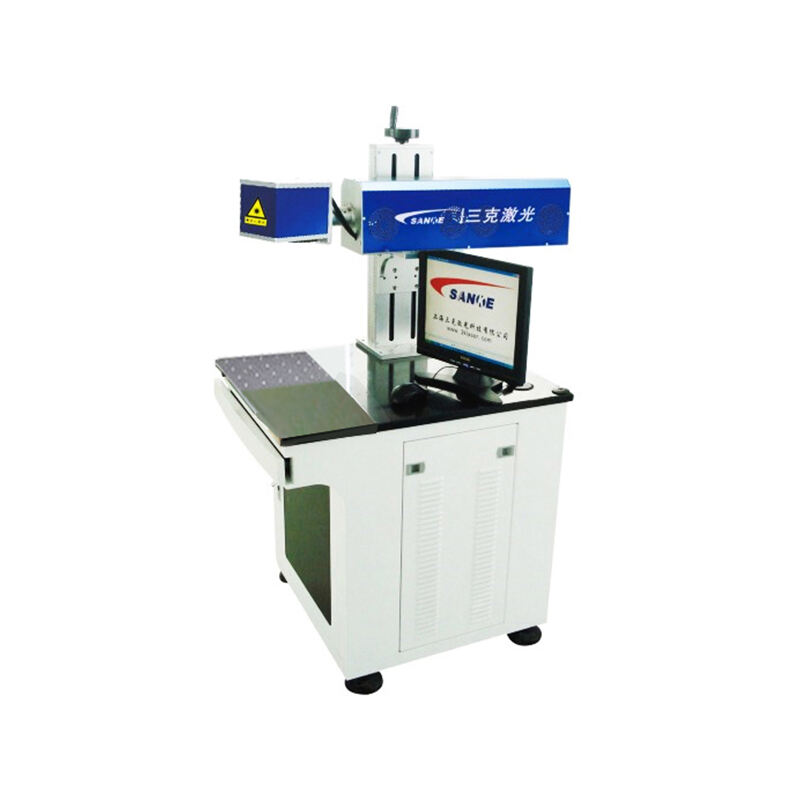
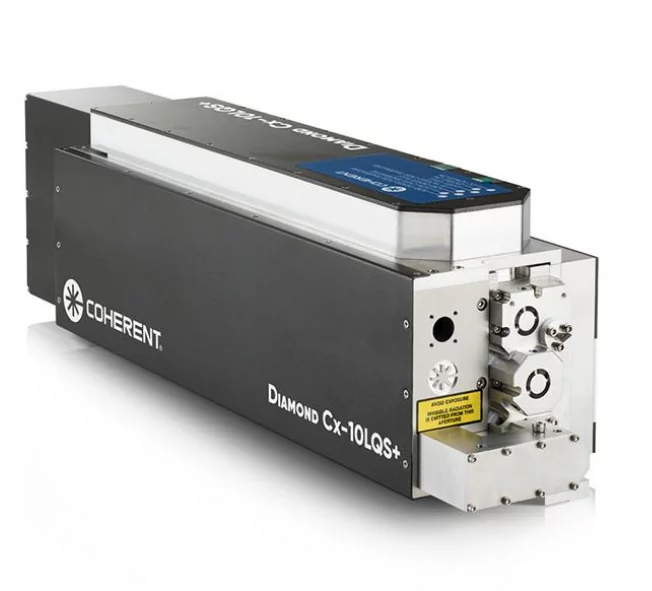
A source of laser light sends rays that represent one of the most significant technological breakthroughs in modern optical engineering. This sophisticated system generates coherent light through stimulated emission of radiation, producing highly focused beams with exceptional precision and intensity. The fundamental principle behind how a source of laser light sends rays involves exciting atoms or molecules within an active medium, causing them to emit photons in a synchronized manner. This process creates light waves that maintain consistent wavelength, phase, and direction, resulting in the characteristic properties that make laser technology so versatile. The core components of a source of laser light sends rays include an active medium, which can be solid, liquid, or gas, a pumping mechanism that provides energy to excite the medium, and an optical resonator consisting of mirrors that amplify the light through repeated reflection. Modern laser systems incorporate advanced control mechanisms that regulate power output, beam diameter, and pulse duration with remarkable accuracy. The technological features of a source of laser light sends rays encompass wavelength tunability, allowing operators to select specific frequencies for different applications, and beam quality optimization that ensures consistent performance across various operating conditions. These systems demonstrate exceptional efficiency in energy conversion, transforming electrical or optical input energy into highly concentrated light beams. The applications of a source of laser light sends rays span numerous industries, from manufacturing and medical procedures to scientific research and telecommunications. In industrial settings, these systems enable precise cutting, welding, and engraving operations on various materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics. Medical applications utilize the focused energy of how a source of laser light sends rays for surgical procedures, dermatological treatments, and diagnostic imaging. Scientific research benefits from the coherent properties of laser light for spectroscopy, interferometry, and particle acceleration studies, while telecommunications infrastructure relies on laser technology for fiber optic communications and data transmission systems.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES